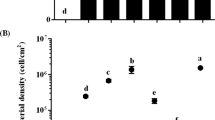
Abstract
Bacterial isolates from multi-species biofilms were identified by 16S rDNA gene sequences and investigated for their inductive effects as monospecific biofilms on larval metamorphosis of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Alteromonas sp. 1 biofilm was found to have inductive activity, which increased with increasing cell density. The cue(s) of Alteromonas sp. 1 biofilm responsible for inducing larval metamorphosis was further investigated. Treatment of the biofilm with formalin, ethanol, heat or ultraviolet irradiation resulted in a significant reduction in the inductive activity of Alteromonas sp. 1, and the crude extract of surface-bound products of the biofilm showed no activity. These results indicated that if the cue was a surface-bound chemical cue, it was unstable, or susceptible to the treatments or the extraction process. On the other hand, the inductive activity of treated biofilms had a linear regression to the cell survival of bacteria, indicating a metabolically active biofilm was a requirement for larval metamorphosis. Conditioned water of the biofilm did not induce larvae to metamorphose. However, larval crawling behavior in the conditioned water was the same as that in the biofilm prior to larval metamorphosis, and significantly different to larval behavior in seawater. This indicated that a potential or partial waterborne cue existed, but remained inactive when alone. A synergistic effect of the conditioned water with formalin-fixed Alteromonas sp. 1 biofilm resulted in a significant increase in larval metamorphosis. Heat treatment and fractionation of the conditioned water demonstrated that the waterborne cue was heat-stable and <3,000 Da in molecular weight. Platinum-coating, Lentil Lectin and Wheat Germ Agglutinin treatments of the formalin-fixed biofilm significantly reduced its synergistic effect with the conditioned water, suggesting that a surface-bound cue was present on the biofilm and that the cue might be associated with the bacterial exopolysaccharide or glycoprotein. Evidence presented here suggests that two chemical cues derived from bacteria act synergistically on larval metamorphosis of Mytilus galloprovincialis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao WY, Satuito CG, Yang JL, Kitamura H (2007) Larval settlement and metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in response to biofilms. Mar Biol 150:565–574
Cáceres-Martínez J, Robledo JA, Figueras A (1994) Settlement and post-larvae behavior of Mytilus galloprovincialis: field and laboratory experiments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 112:107–117
Dahms HU, Dobretsov S, Qian PY (2004) The effect of bacterial and diatom biofilms on the settlement of the bryozoan Bugula neritina. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 313:191–209
Fitt WK, Coon SL, Walch M, Weiner RM, Colwell RR, Bonar DB (1990) Settlement behavior and metamorphosis of oyster larvae (Crassostrea gigas) in response to bacterial supernatants. Mar Biol 106:389–394
García-Lavandeira M, Silva A, Abad M, Pazos AJ, Sánchez JL, Pérez-Parallé ML (2005) Effects of GABA and epinephrine on the settlement and metamorphosis of the larvae of four species of bivalve molluscs. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 316:149–156
Huang S, Hadfield MG (2003) Composition and density of bacterial biofilms determine larval settlement of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 260:161–172
Huggett MJ, Williamson JE, de Nys R, Kjelleberg S, Steinberg PD (2006) Larval settlement of the common Australian sea urchin Heliocidaris erythrogramma in response to bacteria from the surface of coralline algae. Oecologia 149:604–619
Johnson CR, Sutton DC (1994) Bacteria on the surface of crustose coralline algae induce metamorphosis of the crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci. Mar Biol 120:305–310
Johnson CR, Muir DG, Reysenbach AL (1991) Characteristic bacteria associated with surfaces of coralline algae: a hypothesis for bacterial induction of marine invertebrate larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 74:281–294
Khandeparker L, Anil AC, Raghukumar S (2003) Barnacle larval destination: piloting possibilities by bacteria and lectin interaction. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 289:1–13
Kirchman D, Graham S, Reish D, Mitchell R (1982a) Bacteria induce settlement and metamorphosis of Janua (Dexiospira) brasiliensis Grube (Polychaeta: Spirorbidae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 56:153–163
Kirchman D, Graham S, Reish D, Mitchell R (1982b) Lectins may mediate in the settlement and metamorphosis of Janua (Dexiospira) brasiliensis Grube (Polychaeta: Spirorbidae). Mar Biol Lett 3:131–142
Kogure K, Simidu U, Taga N (1979) A tentative direct microscopic method for counting living marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol 25:415–420
Kogure K, Simidu U, Taga N (1984) An improved direct viable count method for aquatic bacteria. Arch Hydrobiol 102:117–122
Lau SCK, Qian PY (2001) Larval settlement in the serpulid polychaete Hydroides elegans in response to bacterial films: an investigation of the nature of putative larval settlement cue. Mar Biol 138:321–328
Lau SCK, Harder T, Qian PY (2003a) Induction of larval settlement in the serpulid polychaete Hydroides elegans (Haswell): role of bacterial extracellular polymers. Biofouling 19(3):197–204
Lau SCK, Thiyagarajan V, Qian PY (2003b) The bioactivity of bacterial isolates in Hong Kong waters for the inhibition of barnacle (Balanus amphitrite Darwin) settlement. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 282:43–60
Leitz T, Wagner T (1993) The marine bacterium Alteromonas espejiana induces metamorphosis of the hydroid Hydractinia echinata. Mar Biol 115:173–178
Maki JS, Mitchell R (1985) Involvement of lectins in the settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Bull Mar Sci 37:675–683
Maki JS, Rittschof D, Schmidt AR, Snyder AG, Mitchell R (1989) Factors controlling attachment of bryozoan larvae: a comparison of bacterial films and unfilmed surfaces. Biol Bull 177:295–302
Negri AP, Webster NS, Hill RT, Heyward AJ (2001) Metamorphosis of broadcast spawning corals in response to bacteria isolated from crustose algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 223:121–131
Neumann R (1979) Bacterial induction of settlement and metamorphosis in the planula larvae of Cassiopea andromeda (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 1:21–28
Olivier F, Tremblay R, Bourget E, Rittschof D (2000) Barnacle settlement: field experiments on the influence of larval supply, tidal level, biofilm quality and age on Balanus amphitrite cyprids. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 199:185–204
Rahim SAKA, Li JY, Kitamura H (2004) Larval metamorphosis of the sea urchins, Pseudocentrotus depressus and Anthocidaris crassispina in response to microbial films. Mar Biol 144:71–78
Ramírez SC, Cáceres-Martínez J (1999) Settlement of the blue mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Larmark on artificial substrates in Bahía de Todos Santos B.C., México. J Shellfish Res 18(1):33–39
Rittschof D (1990) Peptide-mediated behaviors in marine organisms: evidence for a common theme. J Chem Ecol 16(1):261–272
Satuito CG, Natoyama K, Yamazaki M, Fusetani N (1995) Induction of attachment and metamorphosis of laboratory cultured mussel Mytilus edulis galloprovincialis larvae by biofilm. Fisheries Sci 61(2):223–227
Satuito CG, Natoyama K, Yamazaki M, Shimizu K, Fusetani N (1999) Induction of metamorphosis in the pediveliger larvae of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis by neuroactive compounds. Fisheries Sci 65(3):384–389
Satuito CG, Bao WY, Yang JL, Kitamura H (2005) Survival, growth, settlement and metamorphosis of refrigerated larvae of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck and their use in settlement and antifouling bioassays. Biofouling 21(3/4):217–225
Steinberg PD, de Nys R, Kjelleberg S (2001) Chemical mediation of surface colonization. In: McClintock JB, Baker JB (eds) Marine chemical ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 431–460
Szewzyk U, Holmström C, Wrangstadh M, Samuelsson MO, Maki JS, Kjelleberg S (1991) Relevance of the exopolysaccharide of marine Pseudomonas sp. Strain S9 for the attachment of Ciona intestinalis larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 75:259–265
Unabia CRC, Hadfield MG (1999) Role of bacteria in larval settlement and metamorphosis of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar Biol 133:55–64
Weiner RM, Walch M, Labare MP, Bonar DB, Colwell RR (1989) Effect of biofilms of the marine bacterium Alteromonas colwelliana (LST) on set of the oysters Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg, 1793) and C. virginica (Gmelin, 1791). J Shellfish Res 8(1):117–123
Wieczorek SK, Clare AS, Todd CD (1995) Inhibitory and facilitatory effect of biofilms on settlement of Balanus amphitrite larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 119:221–228
Zimmer-Faust RK, Tamburri MN (1994) Chemical identity and ecological implications of a waterborne, larval settlement cue. Limnol Oceanogr 39(5):1075–1087
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. K. Kanai of Nagasaki University for guidance in the identification of the bacteria and the staff of the Nagasaki Prefectural Institute of Fisheries for cooperation in the collection of adult mussels. The authors thank 2 anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. The first author acknowledges Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology for providing a scholarship during the study period. All experiments complied with the current Japanese laws.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Nishida.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, WY., Yang, JL., Satuito, C.G. et al. Larval metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in response to Alteromonas sp. 1: evidence for two chemical cues?. Mar Biol 152, 657–666 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0720-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0720-2