Abstract
The hydraulics of energy dissipation over stepped-gabion weirs is investigated by carrying out a series of laboratory experiments, building models to explain the experimental data, and testing their robustness by using the data reported by other researchers. The experiments comprise: six different stepped-gabion weirs tested in a horizontal laboratory flume, a wide range of discharge values, two weir slopes (V:H): 1:1 and 1:2, and gabion filling material gravel size (porosity equal to 38 %, 40 % and 42 %). These experimental setups were selected to ensure the development of both the nappe and skimming flow regimes within the measured dataset. The models developed for computing energy dissipation over stepped-gabion weirs comprise: multiple regression equations based on dimensional analysis theory, Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Gene Expression Programming (GEP). The analysis shows that the measured data capture both flow regimes and the transition in between them and above all, and by using all of the data, it may be possible to identify the range of each regime. Energy dissipation modelled by the ANN formulation is successful and may be recommended for reliable estimates but those by GEP and regression analysis can still serve for rough-and-ready estimates in engineering applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Abbreviations
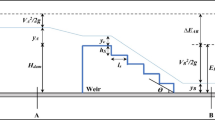
- b :
-
Weir/Spillway width
- E 1 :
-
Energy at the downstream of spillway before hydraulic jump
- E 0 :
-
Total energy at the upstream of Weir/spillway
- ΔE = E 0 − E 1 :
-
Energy difference between upstream and downstream of Weir/spillway
- F r :
-
Froude number = \( {V}_1/\sqrt{g{y}_1} \)
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- h :
-
Each step height
- H w :
-
The height of the crest of Weir/spillway from flume bed
- l :
-
Each step length
- K :
-
Relative energy dissipation defined as K = (E 0 − E 1)/H w
- n :
-
Stone porosity filled in gabion
- q :
-
Discharge per unit width
- Q :
-
Discharge
- R e :
-
Reynolds number = V 1 y i /v
- S :
-
Weir/spillway slope (V: H)
- V α :
-
Approach velocity = q/y
- V 1 :
-
Velocity at the toe of the spillway
- y 0 :
-
Depth of flow about 0.60 m upstream of the spillway above its crest
- y 1 :
-
Depth before hydraulic jump at the Weir/spillway toe
- y 2 :
-
Depth after hydraulic jump, and
- α :
-
Weir/spillway angle (degree) with horizontal line.
References
Chamani MR, Rajaratnam N (1999) Characteristics of skimming flow over stepped spillways. J Hydra Engrg 125(4):361–368
Chanson H (1993) Stepped Spillway Flows and Air Entrainment. Can Journal of Civil Engineering 20(3):422–435
Chanson H, Toombes L (2004) Hydraulics of stepped chutes: The transition flow. J Hydra Res 42(1):43–54
Chinnarasri C, Donjadee S, Israngkura U (2008) Hydraulic characteristics of gabion-stepped weirs. J Hydra Engrg 134(8):1147–1152
Diez-cascon, J., Blanco, I.L., Reviua J., and Garcia, R. (1991). “Studies on the hydraulic behavior of stepped spillways.” Int. Wat. Pow. Dam Cons., 22–26
Ferreira, C., (2001a), “Gene Expression Programming in Problem Solving”, In: 6th Online World Conference on Soft computing in Industrial Applications (Invited Tutorial)
Ferreira C (2001b) Gene Expression Programming: a New Adaptive Algorithm for Solving Problems. Complex Syst 13(2):87–129
Ghorbani, M. A., Khatibi, R., Aytek, A., and Makarynskyy, O. (2010), “Sea Water Level Forecasting Using Genetic Programming and Comparing the Performance with Artificial Neural Networks”, 36:620–627
Ghorbani M.A., Khatibi, R., Asadi, H. And Yousefi, P. (Aug. 2012) “Inter-comparison of an Evolutionary Programming Model of Suspended Sediment Time-series with other Local Models,” Computer and Information Science » Artificial Intelligence » “Genetic Programming - New Approaches and Successful Applications”, book edited by Sebastian Ventura, ISBN 978-953-51-0809-2, Published: October 18, 2012
Kells, J.A. (1994). “Energy dissipation at a gabion weir with throughflow and overflow.” Ann. Conference Can. Soc. Civ. Engrg., Winnipeg, Canada, June 1–4, 26–35
Kocabas F, Kisi O, Ardiclioglu M (2009) An artificial neural network model for prediction of critical submergence for an intake in a stratified fluid media. Civil Engineering & Environmental Systems 26(4):367–375
Markovic M (2012) Multi-criteria Analysis of Hydraulic Structures for River Training Works. Water Resource Management 26:3893–3906
Matos J, Quintela A (1994) Jet flow on stepped spillways. Discussion, J Hydra Engrg 120(2):443–444
Mohamed HI (2010) Flow over gabion weirs. ASCE Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering 136(8):573–577
Ohtsu I, Yasuda Y, Takahshi M (2004) Flow characteristics of skimming flows in stepped channels. J Hyd Eng, ASCE 130(9):860–869
Pegram GGS, Officer AK, Mottram SR (1999) Hydraulic of skimming flow on modeled stepped spillways. J Hydra Engrg 125(5):500–509
Peyras L, Royet P, Degoutte G (1992) Flow and energy dissipation over stepped gabion weirs. J Hydra Engrg 118(5):707–717
Rajaratnam N (1990) Skimming flow in stepped spillway. J Hydra Engrg 116(5):587–591
Rand W (1955) Flow geometry at straight drop spillway. Proc Am Soc Civ Eng 81(Paper 791):1–13
Said A (2006) The Implementation of a Bayesian Network for Watershed Management Decisions. Water Resources Management 20:591–605
Salmasi F (2010) An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for Hydraulics of Flows on Stepped Chutes. European Journal of Scientific Research 45(3):450–457, ISSN 1450–216X
SPSS (Version 17), Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) software version 17
Stephenson, D. (1979). “Gabion Energy Dissipators.” 13th Inter. Cong. Larg. Dams, New Delhi, India, Q50R3, Paris, France, 33–43
Toombes L, Chanson H (2008) Flow patterns in nappe flow regime down low gradient stepped chutes. J Hydra Res 46(1):4–14
Tozzi, M.J. (1992). “Flow characterization/behavior on stepped spillways.” PhD thesis, University of Sao Paulo, Brazil (in Portuguese)
Vesta Services (2000). Qnet2000 Shareware, Vesta Services, Inc., 1001 Green Bay Rd, STE 196, Winnetka, IL 60093
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 168 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatibi, R., Salmasi, F., Ghorbani, M.A. et al. Modelling Energy Dissipation Over Stepped-gabion Weirs by Artificial Intelligence. Water Resour Manage 28, 1807–1821 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0545-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0545-y