Abstract
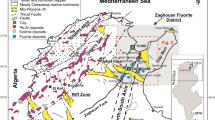
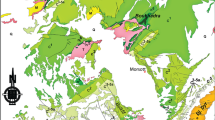
The formation of Parzán fluorite-lead «extension-type» vein (Spanish Central Pyrenees) is related to the post-Hercynian hydrothermal activity widespread not only in the Pyrenees but in Western Europe as well. The lode was later strongly deformed during the Alpine orogeny with textural modifications and destruction of primary fluid inclusions. In order to determine if geochemical signatures of the vein were disturbed during Alpine deformation, post-ore fluid inclusions and quartz oxygen-isotopes have been addressed. Microthermometry and X-ray microanalysis of frozen inclusions confirm the Na-Ca-Cl character of post-ore fluid circulations and indicate that they were originally derived from a single source: Triassic connate waters. Oxygen isotope data on quartz formed during deformation along with trace element geochemistry suggest that the geochemical signatures of the vein (mainly REE and 87Sr/86Sr) were apparently not reset during deformation. The REE content of fluorites is very high (up to 0.12%); the chondrite normalized REE patterns display a continuous decrease from La to Lu. Sulphur isotope data for the Parzán vein is outside the typical “deep seated” range, suggesting dominantly crustal sources of sulphur for sulphides, while formation waters may be proposed for barite. Parzán fluorites have the most radiogenic Sr values of all the investigated fluorite deposits in Central Pyrenees. They scatter in the range of both the igneous rocks and the Cambrian-Ordovician and Triassic detrital sequences of the Parzán area. If REE contents and 87Sr/86Sr ratios reflect the primary stage of vein filling as suggested by the good correlation between both geochemical signatures, the linear array between 87Sr/86Sr and 1/ΣREE is suggestive of a mixing process. The δ34S, δ18O and 87Sr/86Sr parameters in barite, which postdates the fluorite, also provide strong evidence that barite deposition is a result of fluid mixing. Such an interpretation is in line with present-day ideas for the genesis of many of the F-Ba-Pb-Zn vein deposits in the Hercynian belt of Iberia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 June 1997 / Accepted: 10 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanlo, I., Touray, J., Subías, I. et al. Geochemical patterns of a sheared fluorite vein, Parzan, Spanish Central Pyrenees. Mineral. Deposita 33, 620–632 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260050177
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260050177