Abstract
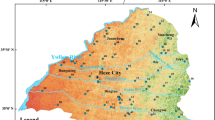
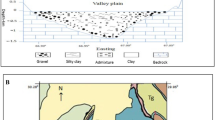
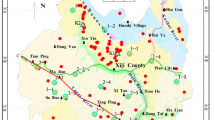
Long-term intake of high-fluoride groundwater causes endemic fluorosis. This study, for the first time, discovered that the salt lake water intrusion into neighboring shallow aquifers might result in elevation of fluoride content of the groundwater. Two cross-sections along the groundwater flow paths were selected to study the geochemical processes controlling fluoride concentration in Yuncheng basin, northern China. There are two major reasons for the observed elevation of fluoride content: one is the direct contribution of the saline water; the other is the undersaturation of the groundwater with respect to fluorite due to salt water intrusion, which appears to be more important reason. The processes of the fluorine activity reduction and the change of Na/Ca ratio in groundwater induced by the intrusion of saline water favor further dissolution of fluorine-bearing mineral, and it was modeled using PHREEQC. With the increase in Na concentration (by adding NaCl or Na2SO4 as Na source, calcium content kept invariable), the increase of NaF concentration was rapid at first and then became slower; and the concentrations of HF, HF −2 , CaF+, and MgF+ were continuously decreasing. The geochemical conditions in the study area are advantageous to the complexation of F− with Na+ and the decline of saturation index of CaF2, regardless of the water type (Cl–Na or SO4–Na type water).















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks D, Reimann C, Royset O, Skarphagen H, Saether OM (1995) Natural concentrations of major and trace elements in some Norwegian bedrock groundwaters. Appl Geochem 10(1):1–16
Botha FS, Van Rooy JL (2001) Affordable water resource development in the northern province, South Africa. J Afr Earth Sci 33(3):687–692
Cao X, Zhao W, Wei J (1997) The formation and distribution of fluoride enriched groundwater in Yuncheng Basin, Shanxi Province, China (in Chinese). Shaxi Hydrotech 116(2):30–33
Carrillo-Rivera JJ, Cardona A, Edmunds WM (2002) Use of abstraction regime and knowledge of hydrogeological conditions to control high fluoride concentration in abstracted groundwater: San Luis Potos basin, Mexico. J Hydrol 261:24–47
Cauley J, Murphy P (1995) Effects of fluoridated drinking water on bone mass and fractures: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 10(7):1076–1086
Choubisa SL (2001) Endemic fluorosis in southern Rajasthan, India. Fluoride 34(1):61–70
Choubisa SL, Sompura K, Choubisa DK, Pandya H, Bhatt SK, Sharma OP, Parmar L (1995) Fluoride content in domestic water resources of Dungarpur districts of Rajasthan. Indian J Environ Health 37:154–160
Frencken JE (1992) Endemic fluorosis in developing countries, causes, effects and possible solutions. NIPG-TNO, Leiden, The Netherlands
Frengstad B, Banks D, Siewers U (2001) The chemistry of Norwegian groundwaters: IV. The dependence of element concentrations in crystalline bedrock groundwaters. Sci Total Environ 277:101–117
Gizaw B (1996) The origin of high bicarbonate and fluoride concentration in waters of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley, East African Rift system. J Afr Earth Sci 22:391–402
Jacobsen SJ, O’Fallon M, Melton LJ (1993) Hip fracture incidence before and after the fluoridation of the public water supply, Rochester, Minnesota. Am J Public Health 83:743–745
Krainov SR, Petrova NG (1976) Fluorine-bearing groundwater, their geochemical characteristics, and the effect on biological processes. Geokhimiya 10:1533–1541
Krainov SR, Zakutin VP (1994) Geochemical and environmental state of groundwater in Russia (the causes and tendencies in the changes of groundwater chemistry). Geokhimiya 3:312–329
Lu X, Zhang S, Zhang J (2004) Surveillance on fluoride during 10 years drinking-water improvement in Yuncheng city. China J End 23(1):53–54
Parkurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations: US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259 (a report)
Shanker R, Thussu JL, Prasad JM (2003) Geothermal studies at Tattapani hot spring area, Sarguja district, central India. Geothermics 16:61–76
Tu VL, Watkins R, Nguyen GK (2006) Distribution and genesis of high-fluoride groundwaters in Ninh Hoa District, Vietnam. Paper presented at the scientific programs of the 7th international symposium on environmental geochemistry, Beijing, 24–27
Wang Z, Xin X, Chang Y (2000) Formation causes and controlling measures of groundwater quality deterioration in Xiezhou area, Yuncheng City. Earth Sci 25(5):477–480 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yiamouyiannis JA, Burk D (1976) Fluoridation of public water systems and cancer death rates in humans. Fed Proc 35:1707
Yun G (2001) Preventive measures against worsening of groundwater quality in Haizhou township (in Chinese). Shanxi Hydraul Eng 2:12–13
Zhang Y (1993) Causes for the rising again of fluoring contents in water in Yuncheng prefecture and determination of effective value of fluorine in water in No.1 endemic area (in Chinese). Hydrogeol Eng Geol 6:53–55
Acknowledgments
The research work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.40425001) and China Geological Survey (No. CGS-200310400009). The manuscript greatly benefited from the constructive comments from prof. Teng Ma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Wang, Y., Li, Y. et al. Enrichment of fluoride in groundwater under the impact of saline water intrusion at the salt lake area of Yuncheng basin, northern China. Environ Geol 53, 795–803 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0692-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0692-z