Abstract
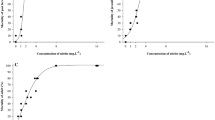
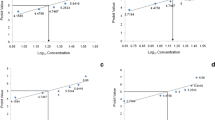
The effects of ammonia and nitrite on vigour, survival rate, moulting rate of zoea of blue swimming crab, Portunus pelagicus, were studied. A total of five nitrite-N treatments (26.67, 53.34, 106.68, 213.36, 426.72 mg/l) and a control (no nitrite-N added) were set up for the acute nitrite-N toxicity experiment; a total of five ammonia-N treatments (8.43, 16.86, 33.72, 67.44, 134.88 mg/l) and a control (no ammonia-N added) were set up for the acute ammonia-N toxicity experiment. The results showed that the vigour, survival rate and moulting rate of zoea of the blue swimming crabs exposed to over 53.34 mg/l were significantly different (P < 0.05) from the control group. The zoea LC50 values (mg/l) of nitrite-N were 179.47, 76.56, 66.70, 37.49, 25.01, 25.35, 25.34 mg/l for 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96 h, respectively. The vigour, survival rate and moulting rate of zoea of the blue swimming crabs exposed to over 16.86 mg/l were significantly different (P < 0.05) from the control group. The zoea LC50 values (mg/l) of ammonia-N were 51.04, 39.62, 38.72, 24.43, 16.90, 13.42, 11.16 mg/l for 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96 h, respectively. The zoeae are highly sensitive to ammonia and nitrite, and the toxicity of ammonia and nitrite on Portunus pelagicus decrease with development of this crab.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brisset P, Versichele D, Bossuyt E, de Ruyck L, Sorgeloos P (1982) High density flow-through culturing of brine shrimp Artemia on inert feeds—preliminary results with a modified culture system. Aqua Eng 1:115–119
Bryars SR, Havenhand JN (2006) Effects of constant and varying temperatures on the development of blue swimmer crab (Portunus pelagicus) larvae: Laboratory observations and field predictions for temperate coastal waters. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 329:218–229
Chen JC, Chen KJ, Liao JM (1989) Joint action of ammonia and nitrite on Artemia nauplii. Aquaculture 77:329–336
Colt J, Tchobanoglous G (1978) Chronic exposure of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, to ammonia: effects on growth and survival. Aquaculture 15:353–372
Hassan R (1995) Early attempts on the culture of swimming crab (Portunus pelagicus Linnaeus) in brackish water ponds. Buletin perikanan. Fisheries bulletin. Department of Fisheries (Malaysia) 97:8
Josileen J, Menon NG (2004) Larval stages of the blue swimmer crab, portunus pelagicus (Linnaeus, 1758) (decapoda, brachyura). Crustaceana 77(7):785–803
Koo JG, Kim SG, Jee JH, Kim JM, Bai SC, Kang JC (2005) Effects of ammonia and nitrite on survival, growth and moulting in juvenile tiger crab, Orithyia sinica (Linnaeus). Aquacult Res 36:79–85
Liao YY, Zeng J (2000) The studies on artificial breeding of Portunus pelagicus in spring. Mar Sci 24(12):10–15 (in Chinese)
Liao YY, Yu B, Dong XX (2001) Study on larval development of Portunus pelagicus. J Oceanogrin Taiwan Strait 20(4):533–546 (in Chinese)
Lin YC, Chen JC (2001) Acute toxicity of ammonia on Litopenaeus vannamei Boone juveniles at different salinity levels. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 259:109–119
Lin HP, Thuet P, Trilles JP, Mounet-Guillaume R, Charmantier G (1993) Effects of ammonia on survival and osmoregulation of various development stages of the shrimp Penaeus japonicus. Mar Biol 117(4):591–598
Lu GT, Wang ZZ, Wang HP, Yuan JY (2006) Acute toxic effects of NaNO2 on Portunus trituberculatus Larvae. J Zhejiang Ocean Univ (Nat Sci) 25(3):244–248 (in Chinese)
Neil LL, Fotedar R, Shelley CC (2005) Effects of acute and chronic toxicity of unionized ammonia on mud crab, Scylla serrata (Forsskål, 1755) larvae. Aquacult Res 36(9):927–932
Ostrenskya A, Wasielesky W (1995) Acute toxicity of ammonia to various life stages of the São Paulo shrimp, Penaeus paulensis Pérez-Farfante, 1967. Aquaculture 132(3–4):339–347
Paterson B, Mann D, Kelly B, Barchiesi M (2007) Limb-loss in pond-reared blue swimmer crabs Portunus pelagicus (L.): effect on growth in an indoor shedding system. Aquacult Res 38(14):1569–1579
Romano N, Zeng CS (2006) The effects of salinity on the survival, growth and haemolymph osmolality of early juvenile blue swimmer crabs, Portunus pelagicus. Aquaculture 260:151–162
Romano N, Zeng CS (2007) Ontogenetic changes in tolerance to acute ammonia exposure and associated gill histological alterations during early juvenile development of the blue swimmer crab, Portunus pelagicus. Aquaculture 266(1–4):246–254
Romano N, Zeng CS (2009) Subchronic exposure to nitrite, potassium and their combination on survival, growth, total haemocyte count and gill structure of juvenile blue swimmer crabs, Portunus pelagicus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(4):1287–1295
Seneriches-Abiera ML, Parado-Estepa F, Gonzales GA (2007) Acute toxicity of nitrite to mud crab Scylla serrata (Forsskal) larvae. Aquacult Res 38(14):1495–1499
Sukumaran KK, Neelakandan B (1997) Age and growth in two marine portunid crabs, Portunus (Portunus) sanguinolentus (Herbst) and Portunus (Portunus) pelagicus (Linnaeus) along the southwest coast of India. Ind J Fish 44(2):111–131
Sukumaran KK, Neelakantan B (1996) Mortality and stock assessment of two marine portunid crabs, Portunus (Portunus) sanguinolentus (Herbst) and Portunus (Portunus) pelagicus (Linnaeus) along the southwest coast of India. Ind J Fish 43(3):225–240
Tabata K (1962) Toxicity of ammonia to aquatic animals with reference to the effect of pH and carbon dioxide. Bull Tokai Reg Fish Res Lab 34:67–74
Wang HY, Wu HL, Wang ZW, Wang XY, Wang SC (2001) Fisheries biology of Portunus pelagicus Linneus initialing investigation. Marine Sci 25(1):36–39 (in Chinese)
Weihrauch D, Morris S, Towle DW (2004) Ammonia excretion in aquatic and terrestrial crabs. J Exp Biol 207:4491–4504
Williams MJ, Primavera JH (2001) Choosing tropical portunid species for culture, domestication and stock enhancement in the Indo-Pacific. Asian Fish Sci 14(2):121–142
Zhao JH, Lam TJ, Guo JY (1997) Acute toxicity of ammonia to the early stage-larvae, juveniles of Eriocheir sinensis H. Milne-Edwards, 1853 (Decapoda: Grapsidae) reared in the laboratory. Aquacult Res 28(7):517–525
Zhao JH, Guo JY, Lam TJ (1998) Lethal doses of ammonia on the late-stage larvae of Chinese mitten-handed crab, Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards), (Decapoda: Grapsidae) reared in the laboratory. Aquacult Res 29(9):635–642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Y.Y., Wang, H.H. & Lin, Z.G. Effect of ammonia and nitrite on vigour, survival rate, moulting rate of the blue swimming crab Portunus pelagicus zoea. Aquacult Int 19, 339–350 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-010-9398-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-010-9398-4