Abstract
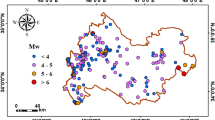
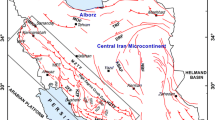
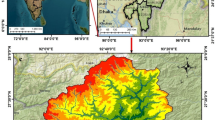
In this study, Dempster–Shafer theory (DST) is integrated into a geographic information system to model vulnerability of the land surface to earthquake events in northwestern Kermanshah Province, Iran, to predict where damage is most likely to occur. DST has never been used to spatially model earthquake vulnerability. To achieve this, data layers for several environmental attributes—aspect, elevation, lithology, slope angle, land use, distance from river courses, distance from roads, and distance from faults—were compiled in ArcGIS 10.2.2 software. Using membership functions, fuzzy maps were generated for each parameter. These fuzzy maps provided input data for the DST model. The predicted values were analyzed and compared at three confidence levels to determine the effectiveness of the model. The results are that 11.14%, 14.14%, and 17.18% (95%, 99%, and 99.5% confidence levels, respectively) of the study area are predicted to be susceptible to earthquakes based on receiver operating characteristic curves. The results also show that, according to the area under the curve (AUC) values (0.967, 0.828, and 0.849 for 95%, 99%, and 99.5% confidence levels, respectively), DST model generates earthquake zoning maps with high accuracy. Therefore, this model can be used for generating earthquake zoning maps with confidence levels that best suit the economic conditions and significance of the region.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaabane SB, Sayadi M, Fnaiech F, Brassart E (2008) Color image segmentation based on Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. In: MELECON 2008-the 14th IEEE mediterranean electrotechnical conference 2008 May 5. IEEE, pp 862–866. https://doi.org/10.1109/MELCON.2008.4618544
Chen D, Dong W, Shah HC (1988) Earthquake recurrence relationships from fuzzy earthquake magnitudes. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 7(3):136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0267-7261(88).80017-4
Cumming G, Fidler F (2005) Interval estimates for statistical communication: Problems and possible solutions. In: IASE/ISI Satellite, pp 1–7
Dempster AP (1968) A generalization of Bayesian inference. J R Stat Soc Series B 30(2):205–232
Dempster AP (2008) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Stud Fuzziness Soft Comput 219:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-44792-4_3
Dezhkam B, Nouri AZ (2018) Dynamic response of nanoparticle-water pipes buried in the soil subjected to far-fault earthquake using numerical method. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 113:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2018.06.002
Erden T, Karaman H (2012) Analysis of earthquake parameters to generate hazard maps by integrating AHP and GIS for K ¨ uçuç¨uçükçekmece region. Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:475–483. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-475-2012
Fernandez VB (2009) Geo—information for measuring vulnerability to earthquakes : a fitness for use approach. https://research.utwente.nl/en/publications/geo-information-for-measuring-vulnerability-to-earthquakes-a-fitn. Accessed 14 Aug 2018.
Helton JC (1997) Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in the presence of stochastic and subjective uncertainty. J Stat Comput Simul. https://doi.org/10.1080/00949659708811803
Karimzadeh S et al (2014) A GIS-based seismic hazard, building vulnerability and human loss assessment for the earthquake scenario in Tabriz. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 66:263–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2014.06.026
Malpica JA, Alonso MC, Sanz MA (2007) Dempster-Shafer Theory in geographic information systems: a survey. Expert Syst Appl 32(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2005.11.011
Martinelli A et al (2008) Building vulnerability assessment and damage scenarios in Celano (Italy) using a quick survey data-based methodology. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng. 28(10–11):875–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2008.03.002
McBratney AB, Odeh IOA (1997) Application of fuzzy sets in soil science: Fuzzy logic, fuzzy measurements and fuzzy decisions. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(97).00017-7
Nazarimofrad E, Zahrai SM (2017) Fuzzy control of asymmetric plan buildings with active tuned mass damper considering soil-structure interaction. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2017.09.020
Pervin Ishita R, Khandaker S (2010) Application of Analytical Hierarchical Process and GIS in earthquake vulnerability assessment: case study of Ward 37 and 69 in Dhaka City, J. Bangladesh Inst. Planners. https://www.bip.org.bd/SharingFiles/journal_book/20130722134714.pdf.
Rahimi Shahid M, Rahimi N (2017) Earthquake hazard zoning using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and GIS techniques (Case study: central part of the Semirom city). Sci J Manag Syst 11(22):109–118. https://doi.org/10.22084/NFAG.2017.10075.1188
Ranjbar HR et al (2017) A GIS-based approach for earthquake loss estimation based on the immediate extraction of damaged buildings. Geomatics Nat Hazards Risk 8(2):772–791. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2016.1265013
Shafer G (1976) Dempster-Shafer Theory. Int J Approx Reason 21(2):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0888-613X(99).00011-0
Shoyaib M, Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Chae O (2012) A skin detection approach based on the Dempster–Shafer theory of evidence. Int J Approx Reason 53:636–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2012.01.003
Tavakoli B, Favakoli A (1993) Estimating the vulnerability and loss functions of residential buildings. Nat Hazards 7(2):155–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00680428
Varma VK, Ferguson I, Wild I (2000) Decision support system for the sustainable forest management. For Ecol Manag 128(1–2):49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(99).00271-6
Xu ZD, Guo YQ (2008) Neuro-fuzzy control strategy for earthquake-excited nonlinear magnetorheological structures. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 28(9):717–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILDYN.2007.10.013
Yagoub MM (2015) Spatio-temporal and hazard mapping of Earthquake in UAE (1984–2012): remote sensing and GIS application. Geoenviron Disasters 2(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-015-0020-y
Yang JL, Tzeng GH (2011) An integrated MCDM technique combined with DEMATEL for a novel cluster-weighted with ANP method. Expert Syst Appl 38(3):1417–1424. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2010.07.048
Yang X, Chen L (2010) Using multi-temporal remote sensor imagery to detect earthquake-triggered landslides. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 12(6):487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAG.2010.05.006
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65).90241-X
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Shiraz University for providing financial support (238726-156) for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.M. contributed to conceptualization, initial methodology and investigation, and formal analysis; H.R.P. contributed to validation of the earthquake-susceptibility maps; and H.R.P. and J.P.T contributed to writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokarram, M., Pourghasemi, H.R. & Tiefenbacher, J.P. Using Dempster–Shafer theory to model earthquake events. Nat Hazards 103, 1943–1959 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04066-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04066-w