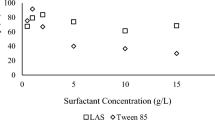
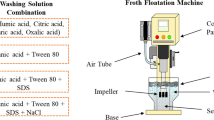
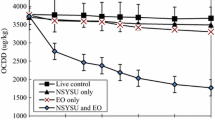
Abstract
PCDD/F-contaminated soil of a coastal region formerly involved in the production of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in Tainan City in southern Taiwan, has drawn wide concern throughout the island. This main goal of this study was to find an effective and environmentally friendly means of removing PCDD/Fs from its contaminated fields. We performed a soil washing experiment with fish extract using a combination of ultrasonification and mechanical double-blade stirring. The experiments were conducted under ambient temperature, at a soil/liquid ratio of 1:2.5, 700 rpm, and over a short duration. This combined method using fish extract removed 94.12% of the pollutant in moderately contaminated soils (5 washing cycles) and 94.51% in highly contaminated soils (10 washing cycles), mostly via particle collision and penetration. These findings highlight the benefits of PCDD/F partitioning between the particles and fish oil extract. This study is the first to use fish oil extract, a natural solvent, to treat soils highly contaminated with dioxins. Because fish oil extract is rich in non-toxic bio-surfactants (e.g., alcohols, acids, ketones, etc.), it may be used in this process to improve bioavailability and bioactivity of the soil making bio-attenuation and full remediation safer and more efficient.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, C. K., Kim, Y. M., Woo, S. H., & Park, J. M. (2008). Soil washing using various nonionic surfactants and their recovery by selective adsorption with activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154(1–3), 153–160.
Alaee, ME 2016. Dioxin and Related Compounds, Switzerland, Springer International Publishing pp.
Almazán-Sánchez, P. T., Cotillas, S., Sáez, C., Solache-Ríos, M. J., Martínez-Miranda, V., Cañizares, P., Linares-Hernández, I., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2017). Removal of pendimethalin from soil washing effluents using electrolytic and electro-irradiated technologies based on diamond anodes. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 213, 190–197.
Barone, G., Giacominelli-Stuffler, R., Garofalo, R., Castiglia, D., & Storelli, M. M. (2014). PCBs and PCDD/PCDFs in fishery products: Occurrence, congener profile and compliance with European Union legislation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 74, 200–205.
Birkett, JW and Lester, JN 2003. Endocrine disrupters in wastewater and sludge treatment processes, Boca Raton, Lewis Pub. pp.
Boening, D. W. (1998). Toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to several ecological receptor groups: A short review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 39(3), 155–163.
Chang, H. J., Wang, S., Li, H. W., Lin, K. H., Chao, C. C., & Lai, Y. C. (2010). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofuran contents in fish and sediment near a pentachlorophenol contaminated site. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 45(8), 923–931.
Collings, A. F., Farmer, A. D., Gwan, P. B., Pintos, A. P. S., & Leo, C. J. (2006). Processing contaminated soils and sediments by high power ultrasound. Minerals Engineering, 19(5), 450–453.
Conte, P., Agretto, A., Spaccini, R., & Piccolo, A. (2005). Soil remediation: Humic acids as natural surfactants in the washings of highly contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 135(3), 515–522.
Czerwinski, F. (2004a). The generation of Mg–Al–Zn alloys by semisolid state mixing of particulate precursors. Acta Materialia, 52(17), 5057–5069.
Czerwinski, F. (2004b). Magnesium alloy particulates for Thixomolding applications manufactured by rapid solidification. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 367(1–2), 261–271.
Feng, D., & Aldrich, C. (2000). Sonochemical treatment of simulated soil contaminated with diesel. Advances in Environmental Research, 4(2), 103–112.
Habe, H., Ide, K., Yotsumoto, M., Tsuji, H., Hirano, H., Widada, J., Yoshida, T., Nojiri, H., & Omori, T. (2001). Preliminary examinations for applying a carbazole-degrader, Pseudomonas sp. strain CA10, to dioxin-contaminated soil remediation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56(5–6), 788–795.
Hasegawa, J., Guruge, K. S., Seike, N., Shirai, Y., Yamata, T., Nakamura, M., Handa, H., Yamanaka, N., & Miyazaki, S. (2007). Determination of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in fish oils for feed ingredients by congener-specific chemical analysis and CALUX bioassay. Chemosphere, 69(8), 1188–1194.
Hosoya, K., Kimata, K., Fukunishi, K., Tanaka, N., Patterson Jr., D. G., Alexander, L. R., Barnhart, E. R., & Barr, J. (1995). Photodecomposition of 1,2,3,4- and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in water-alcohol media on a solid support. Chemosphere, 31(7), 3687–3698.
Hsueh, K. A., Chang, F. C., Wang, H. P., Wang, H. C., Huang, Y. J., Huang, H. L., & Tuan, Y. J. (2013). Enhanced extraction of PAHs hindered in fly ashes with supercritical water. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 73, 116–119.
Huang, R., Huang, K.-L., Lin, Z.-Y., Wang, J.-W., Lin, C., & Kuo, Y.-M. (2013). Recovery of valuable metals from electroplating sludge with reducing additives via vitrification. Journal of Environmental Management, 129, 586–592.
Huang, W. Y., Hung, W. T., Vu, C. T., Chen, W. T., Lai, J. W., & Lin, C. T. (2016). Green and sustainable remediation (GSR) evaluation: Framework, standards, and tool. A case study in Taiwan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(21), 21712–21725.
Hung, P.-C., Chang, S.-H., Ou-Yang, C.-C., & Chang, M.-B. (2016). Simultaneous removal of PCDD/Fs, pentachlorophenol and mercury from contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 144, 50–58.
Hung, W, Huang, W-Y, Lin, C, Vu, CT, Yotapukdee, S, Kaewlaoyoong, A, Chen, J-R and Shen, Y-H 2017, The use of ultrasound-assisted anaerobic compost tea washing to remove poly-chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzo-furans (PCDFs) from highly contaminated field soils, Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Islam, M. N., Jo, Y.-T., & Park, J.-H. (2012). Remediation of PAHs contaminated soil by extraction using subcritical water. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18(5), 1689–1693.
Jonsson, S., Lind, H., Lundstedt, S., Haglund, P., & Tysklind, M. (2010). Dioxin removal from contaminated soils by ethanol washing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1–3), 393–399.
Jung, J., Yang, J.-S., Kim, S.-H., & Yang, J.-W. (2008). Feasibility of micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF) or the heavy metal removal in soil washing effluent. Desalination, 222(1), 202–211.
Kapp Jr., R. W. (2014). CERCLA; revised as the superfund amendments reauthorization act (SARA). In P. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (third edition). Oxford: Academic Press.
Kasai, E., Harjanto, S., Terui, T., Nakamura, T., & Waseda, Y. (2000). Thermal remediation of PCDD/Fs contaminated soil by zone combustion process. Chemosphere, 41(6), 857–864.
Khodadoust, A. P., Bagchi, R., Suidan, M. T., Brenner, R. C., & Sellers, N. G. (2000). Removal of PAHs from highly contaminated soils found at prior manufactured gas operations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 80(1–3), 159–174.
Kim, Y., & Lee, D. (2002). Solubility enhancement of PCDD/F in the presence of dissolved humic matter. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 91(1–3), 113–127.
Kim, Y. J., Lee, D. H., & Osako, M. (2002). Effect of dissolved humic matters on the leachability of PCDD/F from fly ash—laboratory experiment using Aldrich humic acid. Chemosphere, 47(6), 599–605.
Kulkarni, P. S., Crespo, J. G., & Afonso, C. A. M. (2008). Dioxins sources and current remediation technologies—a review. Environment International, 34(1), 139–153.
Kuokka, S., Rantalainen, A. L., & Häggblom, M. M. (2014). Anaerobic reductive dechlorination of 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin- and dibenzofuran-contaminated sediments of the Kymijoki River, Finland. Chemosphere, 98, 58–65.
Lee, C.-C., Guo, Y. L., Kuei, C.-H., Chang, H.-Y., Hsu, J.-F., Wang, S.-T., & Liao, P.-C. (2006). Human PCDD/PCDF levels near a pentachlorophenol contamination site in Tainan, Taiwan. Chemosphere, 65(3), 436–448.
Li, H., Qu, R., Li, C., Guo, W., Han, X., He, F., Ma, Y., & Xing, B. (2014). Selective removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soil washing effluents using biochars produced at different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresource Technology, 163, 193–198.
Liao, PY, Liu, CW and Liu, WY 2016, Bioaccumulation of mercury and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in salty water organisms, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, vol. 188, no. 1.
Lin, D. Y., Shy, C. G., Chen, F. A., Wang, Y. F., Chen, K. C., Hsieh, L. T., Tsai, F. Y., Tsou, T. C., & Chao, H. R. (2013). Use of a highly sensitive recombinant hepatoma cell method to determine dioxin concentrations in samples of fish and crab from a hotspot area. Environ Sci Process Impacts, 15(6), 1264–1270.
Mino, Y., Moriyama, Y., & Nakatake, Y. (2004). Degradation of 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by Fe3+−H2O2 mixed reagent. Chemosphere, 57(5), 365–372.
Mitrou, P. I., Dimitriadis, G., & Raptis, S. A. (2001). Toxic effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related compounds. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 12(5), 406–411.
Nakamiya, K., Furuichi, T., & Ishii, K. (2003). Evaluation of the optimal washing conditions for dioxin-contaminated soils from the circumference of an incinerator. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 5(1), 0063–0068.
Onotri, L., Race, M., Clarizia, L., Guida, M., Alfè, M., Andreozzi, R., & Marotta, R. (2017). Solar photocatalytic processes for treatment of soil washing wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 318, 10–18.
Park, B., & Son, Y. (2017). Ultrasonic and mechanical soil washing processes for the removal of heavy metals from soils. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 35(Part B), 640–645.
Peng, S., Wu, W., & Chen, J. (2011). Removal of PAHs with surfactant-enhanced soil washing: Influencing factors and removal effectiveness. Chemosphere, 82(8), 1173–1177.
Sahle-Demessie, E., Grosse, D. W., & Bates, E. R. (2000). Solvent extraction and soil washing treatment of contaminated soils from wood preserving sites: Bench-scale studies. Remediation Journal, 10(3), 85–109.
Satyro, S., Race, M., Di Natale, F., Erto, A., Guida, M., & Marotta, R. (2016). Simultaneous removal of heavy metals from field-polluted soils and treatment of soil washing effluents through combined adsorption and artificial sunlight-driven photocatalytic processes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 283, 1484–1493.
Son, Y., Cha, J., Lim, M., Ashokkumar, M., & Khim, J. (2011). Comparison of ultrasonic and conventional mechanical soil-washing processes for diesel-contaminated sand. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 50(4), 2400–2407.
Son, Y., Nam, S., Ashokkumar, M., & Khim, J. (2012). Comparison of energy consumptions between ultrasonic, mechanical, and combined soil washing processes. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 19(3), 395–398.
Sponza, D. T., & Gök, O. (2010). Effect of rhamnolipid on the aerobic removal of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and COD components from petrochemical wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 101(3), 914–924.
Stalling, D. L., Norstrom, R. J., Smith, L. M., & Simon, M. (1985). Patterns of PCDD, PCDF, and PCB contamination in Great Lakes fish and birds and their characterization by principal components analysis. Chemosphere, 14(6–7), 627–643.
Suominen, K., Hallikainen, A., Ruokojärvi, P., Airaksinen, R., Koponen, J., Rannikko, R., & Kiviranta, H. (2011). Occurrence of PCDD/F, PCB, PBDE, PFAS, and organotin compounds in fish meal, fish oil and fish feed. Chemosphere, 85(3), 300–306.
Tanaka, F., Fukushima, M., Kikuchi, A., Yabuta, H., Ichikawa, H., & Tatsumi, K. (2005). Influence of chemical characteristics of humic substances on the partition coefficient of a chlorinated dioxin. Chemosphere, 58(10), 1319–1326.
Trellu, C., Mousset, E., Pechaud, Y., Huguenot, D., Van Hullebusch, E. D., Esposito, G., & Oturan, M. A. (2016). Removal of hydrophobic organic pollutants from soil washing/flushing solutions: A critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 306, 149–174.
Ukisu, Y., & Miyadera, T. (2004). Dechlorination of dioxins with supported palladium catalysts in 2-propanol solution. Applied Catalysis A: General, 271(1–2), 165–170.
USEPA 1994, Method 8290A—polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) by high-resolution gas chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRGC/HRMS), United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-07/documents/epa-8290a.pdf. Accessed 16 Mar 2017.
USEPA 1996, Method 3630C—silica gel cleanup, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-3630c-silica-gel-cleanup. Accessed 16 Mar 2017.
USEPA 2007, Method 3550C—ultrasonic extraction, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3550c.pdf. Accessed 16 Mar 2017.
Vallejo, M., Roman, M. F. S., Ortiz, I., & Irabien, A. (2015). Overview of the PCDD/Fs degradation potential and formation risk in the application of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) to wastewater treatment. Chemosphere, 118, 44–56.
Van Den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L. S., Denison, M., De Vito, M., Farland, W., Feeley, M., Fiedler, H., Hakansson, H., Hanberg, A., Haws, L., Rose, M., Safe, S., Schrenk, D., Tohyama, C., Tritscher, A., Tuomisto, J., Tysklind, M., Walker, N., & Peterson, R. E. (2006). The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicological Sciences, 93(2), 223–241.
Van Den, M. B., Birnbaum, L., Bosveld, A. T. C., Brunstrom, B., Cook, P., Feeley, M., Giesy, J. P., Hanberg, A., Hasegawa, R., Kennedy, S. W., Kubiak, T., Larsen, J. C., Van Leeuwen, F. X. R., Liem, A. K. D., Nolt, C., Peterson, R. E., Poellinger, L., Safe, S., Schrenk, D., Tillitt, D., Tysklind, M., Younes, M., Waern, F., & Zacharewski, T. (1998). Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environmental Health Perspectives, 106(12), 775–792.
Vieira Dos Santos, E., Sáez, C., Cañizares, P., Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2017). Treating soil-washing fluids polluted with oxyfluorfen by sono-electrolysis with diamond anodes. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 34, 115–122.
Viglianti, C., Hanna, K., De Brauer, C., & Germain, P. (2006). Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aged-contaminated soil using cyclodextrins: Experimental study. Environmental Pollution, 140(3), 427–435.
Weitzman, L. 1984. On-site removal of PCB and dioxins from soils. USA patent application US 06/675,823. 5/5/1987.
Zhang, Y.-f., Liu, Y.-b., Cao, Z.-y., & Zhang, L. (2010). Microstructure transformation of deformed AZ91D during isothermal holding. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 20(1), 14–21.
Zhao, D., Zheng, Y., Li, M., Baig, S. A., Wu, D., & Xu, X. (2014). Catalytic dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Ni/Fe nanoparticles prepared in the presence of ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 21(5), 1714–1721.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the reviewers whose knowledgeable comments and thoughtful suggestions have largely contributed to the improvement of the quality of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vu, C.T., Lin, C., Hung, W. et al. Ultrasonic Soil Washing with Fish Oil Extract to Remove Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), Dibenzofurans (PCDFs) from Highly Contaminated Field Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 343 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3534-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3534-y