Abstract
Purpose
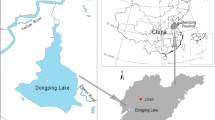
Organophosphorus pesticides (OPs) are significant stressors in the aquatic ecosystem of lakes due to their extensive use in agriculture. To understand the potential ecotoxicological risk of OPs, we examined the occurrence, distribution, and sources of 12 selected OPs in surface and core sediment samples collected around Chaohu Lake, one of the most eutrophic lakes in Eastern China.
Materials and methods
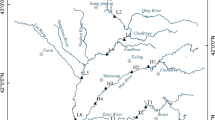
Eighteen surface sediments and four sediment cores were sampled from an important inflowing river and four main river estuaries around Chaohu Lake, respectively. All samples were analyzed for 12 selected OPs using a gas chromatograph equipped with a mass spectrometer.
Results and discussion
The results show that two thirds of the selected OPs were frequently detected around the lake, with detection frequencies of more than 60 %. Dichlorvos was the predominant OP, comprising 89.6 % of the total concentration of the 12 OPs (defined as Σ12OP) in all samples. Σ12OP in surface sediment and in core sediments ranged from 0.50 to 6.45 and 0.27 to 23.33 ng g−1 dry weight, respectively. High concentrations of Σ12OP were found in estuaries of rivers flowing from agricultural lands, indicating that the selected OPs were mostly due to cultivation, and the vertical distribution of OPs in core sediments clearly showed the application history of OPs over the past few decades. The intercorrelation between OPs was likely affected by their sources, degradation rates, and deposition pathways. The poor correlation between OPs and total organic carbon (TOC) in the core sediments of Chaohu Lake might be ascribed to multiple sources of the TOC in Chaohu Lake.
Conclusions
Despite previous studies demonstrated that most OPs were not detectable in bottom sediments due to their high water solubilities and reduced persistence, in the present study, we found that most of the selected OPs were frequently detected in bottom sediment samples collected around Chaohu Lake, which have been identified with long-term eutrophication, suggesting that the OPs likely migrated from the water to the bottom sediment due to the occurrence of massive amounts of phytoplankton. Therefore, the environmental behavior and fate of OPs in a eutrophic lake require more attention given their ecotoxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu V, Unnikrishnan P, Anu G, Nair SM (2011) Distribution of organophosphorus pesticides in the bed sediments of a backwater system located in an agricultural watershed: influence of seasonal intrusion of seawater. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:597–609
Chowdhury MAZ, Banik S, Uddin B, Moniruzzaman M, Karim N, Gan SH (2012) Organophosphorus and carbamate pesticide residues detected in water samples collected from paddy and vegetable fields of the Savar and Dhamrai Upazilas in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Res Public Health 9:3318–3329
Cole MA, Elliott RJR, Wu S (2008) Industrial activity and the environment in China: an industry-level analysis. China Econ Rev 19:393–408
Essumang DK, Togoh GK, Chokky L (2009) Pesticide residues in the water and fish (lagoon tilapia) samples from lagoons in Ghana. B Chem Soc Ethiopia 23:19–27
Gao JJ, Liu LH, Liu XR, Zhou HD, Lu J, Huang SB, Wang ZJ (2009) The occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphorous pesticides in Chinese surface water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:223–229
Gitahi SM, Harper DM, Muchiri SM, Tole MP, Ng’ang’a RN (2002) Organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticide concentrations in water, sediment, and selected organisms in Lake Naivasha (Kenya). Hydrobiologia 488:123–128
Glaser LC (1999) Chapter 39: organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. In: Ciganovich EA (ed), Field manual of wildlife diseases: general field procedures and diseases of birds, Washington, DC, pp 287−294
He H-W (2008) Current situation and development trend of organophosphorous insecticides industry. World Pesticides 30:29–30
He KB, Huo H, Zhang Q (2002) Urban air pollution in China: current status, characteristics, and progress. Annu Rev Energy Environ 27:397–431
He W, Qin N, He Q-S, Wang Y, Kong X-Z, Xu F-L (2012) Characterization, ecological and health risks of DDTs and HCHs in water from a large shallow Chinese lake. Ecol Inform 12:77–84
Hintzen EP, Lydy MJ, Belden JB (2009) Occurrence and potential toxicity of pyrethroids and other insecticides in bed sediments of urban streams in central Texas. Environ Pollut 157:110–116
Hwang HM, Green PG, Holmes RW (2009) Anthropogenic impacts on the quality of streambed sediments in the lower Sacramento River watershed. Calif J Environ Sci Health Part A 44:1–11
Kumar B, Gaur R, Goel G, Mishra M, Prakash D, Singh SK, Lal RB, Kumar S, Sharma CS (2011) Distribution of pesticides in sediments from municipal drains in Delhi, India. Asian J Sci Res 4:271–280
Li H, Tyler Mehler W, Lydy MJ, You J (2011) Occurrence and distribution of sediment-associated insecticides in urban waterways in the Pearl River Delta, China. Chemosphere 82:1373–1379
Newhart K (2006) Environmental fate of malathion, California Environmental Protection Agency
Nizzetto L, Gioia R, Li J, Borgå K, Pomati F, Bettinetti R, Dachs J, Jones KC (2012) Biological pump control of the fate and distribution of hydrophobic organic pollutants in water and plankton. Environ Sci Technol 46:3204–3211
Pehkonen SO, Zhang Q (2010) The degradation of organophosphorus pesticides in natural waters: a critical review. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 32:17–72
Schell LM, Denham M (2003) Environmental pollution in urban environments and human biology. Annu Rev Anthropol 32:111–134
Schiff K, Sutula M (2004) Organophosphorus pesticides in storm-water runoff from southern California (USA). Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1815–1821
Schiff KC, Tiefenthaler LL (2003) Contributions of organophosphorus pesticides from residential land uses during dry and wet weather, Southern California Coastal Water Research Project
Shang G-P, Shang J-C (2005) Causes and control countermeasures of eutrophication in Chaohu Lake, China. Chinese Geogr Sci 15:348–354
Shang G-P, Shang J-C (2007) Spatial and temporal variations of eutrophication in Western Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Monitor Assess 130:99–109
Starner K, Kuivila KM, Jennings B, Moon GE (1999) Degradation rates of six pesticides in water from the Sacramento River, California, U.S. Geological Survey Toxic Substances Hydrology Program--Proceedings of the Technical Meeting Charleston South Carolina
Statistical Bureau of Anhui Province (2013) Anhui Statistical Yearbook, Hefei
Statistical Bureau of Hefei (2012) Hefei Statistical Yearbook, Hefei
Tang W, Shan B, Zhang H, Mao Z (2010) Heavy metal sources and associated risk in response to agricultural intensification in the estuarine sediments of Chaohu Lake Valley, East China. J Hazard Mater 176:945–951
Wang J-Z, Li H-Z, You J (2012a) Distribution and toxicity of current-use insecticides in sediment of a lake receiving waters from areas in transition to urbanization. Environ Pollut 161:128–133
Wang J-Z, Zhang K, Liang B (2012b) Tracing urban sewage pollution in Chaohu Lake (China) using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) as a molecular marker. Sci Total Environ 414:356–363
Wang S-H, Jiang X, Jin X-C (2011) Classification and pollution characteristic analysis for inflow rivers of Chaohu Lake. Environ Sci 32:2834–2839
Xia J, Zhang L, Liu CM, Yu JJ (2007) Towards better water security in North China. Water Resour Manag 21:233–247
Yang C-M, Xu C, Yin D-Q, Li J-H (2011) Phosphorus forms and vertical distribution in sediments of urban rivers in Chaohu City. J Tongji Univ (Natl Sci) 39:1832–1837
Yang C-M, Zhang F, Xu C (2013) Chemical speciation and vertical distribution characteristics of heavy metals in sediment cores of an urban rivers from a typical city in Chaohu lake watershed. J Tongji Univ (Natl Sci) 41:1404–1410
Yang LJ, Li XQ, Crusius J, Jans U, Melcer ME, Zhang PF (2007) ENVR 14-Persistent chlordane concentrations in Long Island Sound sediment: implications from chlordane, 210Pb and 137Cs depth profiles, Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc
Yao S-C, Li S-J (2004) Sedimentary records of eutrophication for the last 100 years in Chaohu Lake. Acta Sedimentol Sin 22:343–347
Yu HY, Bao LJ, Liang Y, Zeng EY (2011) Field validation of anaerobic degradation pathways for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and 13 metabolites in marine sediment cores from China. Environ Sci Technol 45:5245–5252
Zhang G, Parker A, House A, Mai B-X, Li X-D, Kang Y-H, Wang Z-S (2002a) Sedimentary records of DDT and HCH in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Sci Technol 36:3671–3677
Zhang H, Shan BQ (2008a) Historical distribution and partitioning of phosphorus in sediments in a agricultural watershed in the Yangtze-Huaihe region, China. Environ Sci Technol 42:2328–2333
Zhang H, Shan BQ (2008b) Historical records of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and the relationship with agricultural intensification in the Yangtze-Huaihe region, China. Sci Total Environ 399:113–120
Zhang ZL, Hong HS, Zhou JL, Yu G (2002b) Occurrence and behaviour of organophosphorus insecticides in the River Wuchuan, southeast China. J Environ Monit 4:498–504
Acknowledgments
This project was Sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41390240 and 41130206), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2012ZX07503-003-002), and Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (2013JYLH0773). Many thanks go to Zai-Cheng He from Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, China Academy of Science, for organic carbon analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jan Schwarzbauer
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 168 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Zhang, S., Ren, C. et al. Residues of organophosphorus insecticides in sediment around a highly eutrophic lake, Eastern China. J Soils Sediments 15, 436–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-1011-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-1011-4