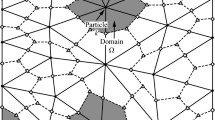
Abstract
In this study, a simple PFEM approach for analyzing large deformation problems in geotechnical practice is implemented in the commercial FEM package Abaqus. The main feature of the proposed Abaqus-PFEM approach lies in its capability to absorb the advantages of the functionality available in Abaqus and integrate them into PFEM with a single Python script, which leads to a considerable reduction in coding work. By utilizing the built-in functions in Abaqus to fulfil the standard incremental FEM analysis, as well as the powerful mesh-to-mesh solution mapping technique, the proposed Abaqus-PFEM approach allows for the large deformation analysis automatically running with a single Python script and requires no intervention from the user. The accuracy of the proposed Abaqus-PFEM approach is firstly validated through a simple elastic cantilever beam bending problem. Then, the performance and robustness of the proposed Abaqus-PFEM approach are further examined by three illustrative numerical examples: penetration of rigid footing, penetration of T-bar and pipeline–soil interaction problem. The numerical results demonstrate that the proposed Abaqus-PFEM approach as a powerful and easily extensible numerical tool is capable of handling large deformation and soil–structure interaction problems in geotechnical engineering, and consequently, it offers an alternative way to tackle such problems.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABAQUS (2016) ABAQUS analysis user’s manual. Version 2016. Dassault Systemes Simulia Corp
Bui HH, Fukagawa R, Sako K, Ohno S (2008) Lagrangian meshfree particles method (SPH) for large deformation and failure flows of geomaterial using elastic-plastic soil constitutive model. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 32(12):1537–1570
Carbonell JM, Oñate E, Suárez B (2010) Modeling of ground excavation with the particle finite-element method. J Eng Mech 136(4):455–463
Carbonell JM, Oñate E, Suárez B (2013) Modelling of tunnelling processes and rock cutting tool wear with the particle finite element method. Comput Mech 52(3):607–629
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, Sorbino G, Piciullo L (2014) SPH run-out modelling of channelised landslides of the flow type. Geomorphology 214:502–513
Peng C, Bauinger C, Szewc K, Wu W, Cao H (2019) An improved predictive-corrective incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for fluid flow modelling. J Hydrodyn 31(4):654–668
Peng C, Wang S, Wu W, Yu H-S, Wang C, Chen J-Y (2019) LOQUAT: an open-source GPU-accelerated SPH solver for geotechnical modeling. Acta Geotechnica 14(5):1269–1287
Dávalos C, Cante J, Hernández JA, Oliver J (2015) On the numerical modeling of granular material flows via the Particle Finite Element Method (PFEM). Int J Solids Struct 71:99–125
Dong Y (2020) Reseeding of particles in the material point method for soil–structure interactions. Comput Geotech 127:103716
Dong Y, Grabe J (2018) Large scale parallelisation of the material point method with multiple GPUs. Comput Geotech 101:149–158
Dong Y, Wang D, Randolph M (2015) A GPU parallel computing strategy for the material point method. Comput Geotech 66:31–38
Einav I, Randolph MF (2005) Combining upper bound and strain path methods for evaluating penetration resistance. Int J Numer Methods Eng 63(14):1991–2016
Hibbitt K. ABAQUS/Standard User’s Manual
Hu Y, Randolph MF (1998) H-adaptive FE analysis of elasto-plastic non-homogeneous soil with large deformation. Comput Geotech 23(1–2):61–83
Hu Y, Randolph MF (1998) A practical numerical approach for large deformation problems in soil. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 22(5):327–350
Kardani M, Nazem M, Carter JP, Abbo AJ (2015) Efficiency of high-order elements in large-deformation problems of geomechanics. Int J Geomech 15(6):04014101
Larese A, Rossi R, Oñate E, Idelsohn SR (2012) A coupled PFEM-Eulerian approach for the solution of porous FSI problems. Comput Mech 50(6):805–819
Luo Y, Huang Y (2020) Effect of open-framework gravel on suffusion in sandy gravel alluvium. Acta Geotech 15(9):2649–2664
Luo Y, Luo B, Xiao M (2020) Effect of deviator stress on the initiation of suffusion. Acta Geotech 15:1607–1617
Meyerhof GG (1951) The ultimate bearing capacity of foudations. Geotechnique 4(4):301–332
Molstad TK (1977) Finite deformation analysis using the finite element method. University of British Columbia, Vancouver
Monforte L, Carbonell JM, Arroyo M, Gens A (2016) Performance of mixed formulations for the particle finite element method in soil mechanics problems. Comput Particle Mech 4:1–16
Monforte L, Arroyo M, Carbonell JM, Gens A (2017) Numerical simulation of undrained insertion problems in geotechnical engineering with the Particle Finite Element Method (PFEM). Comput Geotech 82:144–156
Monforte L, Arroyo M, Carbonell JM, Gens A (2018) Coupled effective stress analysis of insertion problems in geotechnics with the Particle Finite Element Method. Comput Geotech 101:114–129
Nazem M, Sheng D, Carter JP (2006) Stress integration and mesh refinement for large deformation in geomechanics. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65(7):1002–1027
Nazem M, Carter JP, Airey DW (2009) Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian method for dynamic analysis of geotechnical problems. Comput Geotech 36(4):549–557
Oñate E, Idelsohn SR, Del Pin F, Aubry R (2004) The particle finite element method: an overview. Int J Comput Methods 1(2):267–307
Oñate E, Idelsohn SR, Celigueta MA, Rossi R (2008) Advances in the particle finite element method for the analysis of fluid-multibody interaction and bed erosion in free surface flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197(19–20):1777–1800
Oñate E, Celigueta MA, Idelsohn SR, Salazar F, Suárez B (2011) Possibilities of the particle finite element method for fluid-soil-structure interaction problems. Comput Mech 48(3):307–318
Pastor M, Blanc T, Haddad B, Petrone S, Sanchez Morles M, Drempetic V et al (2014) Application of a SPH depth-integrated model to landslide run-out analysis. Landslides 11(5):793–812
Prandtl L (1921) Hauptaufsätze: Über die Eindringungsfestigkeit (Härte) plastischer Baustoffe und die Festigkeit von Schneiden. ZAMM J Appl Math Mech Z Angew Math Mech 1(1):15–20
Qiu G, Henke S, Grabe J (2011) Application of a Coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian approach on geomechanical problems involving large deformations. Comput Geotech 38(1):30–39
Rodriguez JM, Carbonell JM, Cante JC, Oliver J (2016) The particle finite element method (PFEM) in thermo-mechanical problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 107(9):733–785
Salazar F, Irazábal J, Larese A, Oñate E (2016) Numerical modelling of landslide-generated waves with the particle finite element method (PFEM) and a non-Newtonian flow model. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 40(6):809–826
Shan Z, Zhang W, Wang D, Wang L (2019) Numerical investigations of retrogressive failure in sensitive clays: revisiting 1994 Sainte-Monique slide, Quebec, Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01567-4
Shewchuk JR (1996) Triangle: engineering a 2D quality mesh generator and Delaunay triangulator. In: Lin MC, Manocha D (eds) Applied computational geometry: towards geometric engineering. Springer, Berlin
Silva MVD, Krabbenhoft K, Lyamin AV, Sloan SW (2011) Rigid-plastic large-deformation analysis of geotechnical penetration problems. In: Proceedings of 13th IACMAG conference, pp 42–47
Soga K, Alonso E, Yerro A, Kumar K, Bandara S (2015) Trends in large-deformation analysis of landslide mass movements with particular emphasis on the material point method. Gotechnique 66:248–273
Sołowski WT, Sloan SW (2015) Evaluation of material point method for use in geotechnics. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 39(7):685–701
Sulsky D, Chen Z, Schreyer HL (1994) A particle method for history-dependent materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 118(1–2):179–196
Susan Hert, Seel M. dD Convex Hulls and Delaunay Triangulations. CGAL User and Reference Manual. 5.1 ed2020
Tian Y, Cassidy MJ, Randolph MF, Wang D, Gaudin C (2014) A simple implementation of RITSS and its application in large deformation analysis. Comput Geotech 56:160–167
Ullah SN, Hou LF, Satchithananthan U, Chen Z, Gu H (2018) A 3D RITSS approach for total stress and coupled-flow large deformation problems using ABAQUS. Comput Geotech 99:203–215
Wang S, Wu W (2020) A simple hypoplastic model for overconsolidated clays. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01000-z
Wang D, Bienen B, Nazem M, Tian Y, Zheng J, Pucker T et al (2015) Large deformation finite element analyses in geotechnical engineering. Comput Geotech 65:104–114
Wang S, Wu W, Zhang D, Kim J R (2020) Extension of a basic hypoplastic model for overconsolidated clays. Comput Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103486
Wu Y, Li N, Wang X, Cui J, Chen Y, Wu Y, Yamamoto H (2020) Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of calcareous sand retrieved from South China Sea. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105932
Wu Y, Yamamoto H, Cui J, Cheng H (2020) Influence of load mode on particle crushing characteristics of silica sand at high stresses. Int J Geomech 20(3):04019194
Xu C, Kong UOH (2017) Numerical modeling of object penetration in geotechnical engineering. University of Hong Kong Libraries, Pok Fu Lam
Yuan W-H, Zhang W, Dai B-B, Wang Y (2019) Application of the particle finite element method for large deformation consolidation analysis. Eng Comput 36:3138–3163
Yuan W-H, Wang B, Zhang W, Jiang Q, Feng X-T (2019) Development of an explicit smoothed particle finite element method for geotechnical applications. Comput Geotech 106:42–51
Yuan W-H, Liu K, Zhang W, Dai B, Wang Y (2020) Dynamic modeling of large deformation slope failure using smoothed particle finite element method. Landslides 17:1591–1603
Zhang X, Krabbenhoft K, Pedroso DM, Lyamin AV, Sheng D, da Silva MV et al (2013) Particle finite element analysis of large deformation and granular flow problems. Comput Geotech 54:133–142
Zhang X, Krabbenhoft K, Sheng D (2014) Particle finite element analysis of the granular column collapse problem. Granul r Matter 16(4):609–619
Zhang X, Krabbenhoft K, Sheng D, Li W (2015) Numerical simulation of a flow-like landslide using the particle finite element method. Comput Mech 55(1):167–177
Zhang X, Sheng D, Sloan SW, Bleyer J (2017) Lagrangian modelling of large deformation induced by progressive failure of sensitive clays with elastoviscoplasticity. Int J Numer Methods Eng 112(8):963–989
Zhang X, Sloan SW, Oñate E (2018) Dynamic modelling of retrogressive landslides with emphasis on the role of clay sensitivity. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 42(15):1806–1822
Zhang W, Yuan W, Dai B (2018) Smoothed particle finite-element method for large-deformation problems in geomechanics. Int J Geomech 18(4):04018010
Zhang X, Oñate E, Torres SAG, Bleyer J, Krabbenhoft K (2019) A unified Lagrangian formulation for solid and fluid dynamics and its possibility for modelling submarine landslides and their consequences. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 343:314–338
Zhang X, Wang L, Krabbenhoft K, Tinti S (2019) A case study and implication: particle finite element modelling of the 2010 Saint-Jude sensitive clay landslide. Landslides 17:1117–1127
Zhang W, Zhong Z, Peng C, Yuan W, Wu W (2021) GPU-accelerated smoothed particle finite element method for large deformation analysis in geomechanics. Comput Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103856
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by the National key technologies Research & Development program (Grant No. 2017YFC1502603), the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 41807223, No. 51908175 and No. 52078507), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2018A030310346), and the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Innovation Project of Guangdong (No. 2020-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, WH., Wang, HC., Zhang, W. et al. Particle finite element method implementation for large deformation analysis using Abaqus. Acta Geotech. 16, 2449–2462 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01124-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01124-2