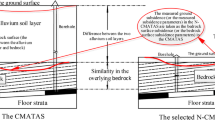
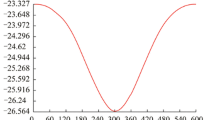
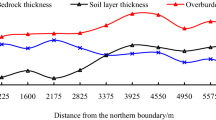
Abstract
Based on a wealth of measured data and the special occurrence condition of coal seam in the Huainan coal mining area of China, this paper proposes a new idea, which is to first separate the overlying bedrock and quaternary alluvium upon coal seam, then study regularities of mining subsidence, respectively, and finally, make a comprehensive research. A method of combining the physical simulation, theoretical analysis, and experimental data is adopted; the internal mechanism behavior and the characteristics of the surface subsidence in coal mining areas with thick alluvium are investigated. The results show that the subsidence in thick alluvium coal mining areas consists of four parts: the subsidence of alluvium soil following the bedrock subsidence caused by coal mining; the synergy subsidence between alluvium soil and bedrock; the subsidence due to groundwater loss and consolidation of the alluvium soil in coal mining area; and the compacting subsidence of shallow soil under the disturbance of coal mining. This theory can be used to completely explain the particularity of surface subsidence in coal mining areas with thick alluvium and provide the basis for establishing the prediction model.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady BHG, Brown ET (2004) ROCK mechanics for underground mining, 3rd edn. Springer, Dordrecht
Budhu M, Adiyaman IB (2009) Mechanics of land subsidence due to groundwater pumping. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 34(14):1459–1478. doi:10.1002/nag.863
Chai J, Shen S, Zhu H, Zhang X (2004) Land subsidence due to groundwater drawdown in Shanghai. Geotechnique 54(01):1143–1147
Cui X, Miao X, Wang J, Yang S, Liu H, Song Y, Liu H, Hu X (2000) Improved prediction of differential subsidence caused by underground mining. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37:615–627
Cui X, Wang JC, Liu Y (2001) Prediction of progressive surface subsidence above longwall coal mining using a time function. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 38:1057–1063
Gao M, Yu Z (2007) Repetitive mining subsidence with thick soil layers and steep seam. J China Coal Soc 32(04):347–352 (in Chinese)
Ge X, Yu G (2006) Influence of underground mining on ground surface and railway bridge under thick alluvium. J China Univ Min Technol 16(01):97–100
Hao Q (1988) Void diffusion model for mined strata and analysis of influence of void sources. J China Univ Min Technol 02:30–36 (in Chinese)
Hao Q, Ma W (1985) On the methods of ground subsidence prediction. J China Univ Min Technol 02:37–42 (in Chinese)
Hao Q, Ma W (1986) The optimum from of weibull distribution subsidence equation and its application in surface subsidence calculation. J China Univ Min Technol 03:32–42 (in Chinese)
He G, Yang L, Ling G, Jia C, Hong D (1991) Mining subsidence science. China university of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Hu RL, Yue ZQ, Wang LC, Wang SJ (2004) Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng Geol 76(1–2):65–77. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.06.006
Huayang D, Xugang L, Jiyan L, Yixin L, Yameng Z, Weinan D, Yinfei C (2010) Model study of deformation induced by fully mechanized caving below a thick loess layer. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(6):1027–1033. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.005
Hugo A, Loaiciga FA (2013) Consolidation settlement in aquifers caused by pumping. J Geotech Geoenviron 139(07):1191–1204. doi:10.1061/(asce)gt.19435606.0000836
Industry SBOC (2004) The regulation of leaving coal pillar and mining coal of holding under the buildings, water bodies, railways and the main roadway. Coal Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Kratzsch H (1983) Mining subsidence engineering. Springer, Berlin
Li W, Yu S (1997) Engineering geological characteristics and mechanism of deformation due to water loss of the soil mass at depths in Xuhuai mine area. J China Coal Soc 22(01):355–360 (in Chinese)
Liang Q, Wen X, He G, Chen Q, Yang J (2007) Study on calculation methods for surface subsidence caused by water loss of clay. J Min Saf Eng 24(01):105–108 (in Chinese)
Litwiniszyn J (2000) The influence of the rate of mining operations on the development of subsidence troughs. Arch Min Sci 45:323–331
Liu Y, Dai H, Jiang Y (2012) Model test for mining-induced movement law of rock and soil mass under thick unconsolidated layers. J Min Saf Eng 29(05):268–272 (in Chinese)
Luo J (1982) Determination of the interface of fractured water-conducting zone by drilling boreholes. Coal Geol Explor 01:53–56 (in Chinese)
Ma L, Zhang D, Sun G, Cui T, Zhou T (2013) Thick alluvium full-mechanized caving mining with large mining height face roof control mechanism and practice. J China Coal Soc 38(02):199–203 (in Chinese)
Miao X, Cui X, Wang Ja XJ (2011) The height of fractured water-conducting zone in undermined rock strata. Eng Geol 120(1–4):32–39. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.03.009
Ortega Guerrero A, Rudolph DL, Cherry JA (1999) Analysis of long-term land subsidence near Mexico City: field investigations and predictive modeling. Water Resour Res 35(11):3327–3341. doi:10.1029/1999wr900148
Peng SS (1992) Surface subsidence engineering. Littleton Society for Mining, Metallurgy
Phienwej N, Giao PH, Nutalaya P (2006) Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng Geol 82(4):187–201. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.10.004
Shen SL, Xu YS (2011) Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can Geotech J 48(9):1378–1392. doi:10.1139/t11-049
Sui W (1992) Mechanism and prediction of soil mass deformation due to mining subsidence. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Sui W, Di Q (1999) Study on interaction between soil mass deformation and pore pressure during subsidence by mining. J Eng Geol 07(04):303–307 (in Chinese)
Tan Z, Deng K, Yang J (2002) Research on ground movement laws for strip mining under thick alluvium. J China Univ Min Technol 12(01):61–64
Wang J, Li Y, Zhou X, Wu L, Wei S (1997) Ground movement caused by mining under thick alluvium. J China Coal Soc 22(01):18–21 (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Deng K, Wu K, Guo G (2003) On the dynamic mechanics model of mining subsidence. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 22(03):352–357 (in Chinese)
Wu K, Ge J, Wang LD, Zhou M (1998) Unify method of mining subsidence prediction. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Wu K, Deng K, Zhou M, Huang Z, Zheng Y, Wang Z (1999) The analysis of monitor conclusion about overburden displacement under condition of fully mechanized sublevel caving. J China Coal Soc 24(01):21–24 (in Chinese)
Wu K, Wang Y, Deng K (2000) Application for dynamic mechanics model of overlying strata movement and damage above goaf. J China Univ Min Technol 29(01):34–36 (in Chinese)
Wu K, Jin J, Dai Z, Jiang J (2002) The experimental study on the transmit of the mining subsidence in soil. J China Coal Soc 27(06):601–603 (in Chinese)
Xu Y, Zhang Y (2002) Deformation characteristics of thick unconsolidated layers due to mining by UDEC. J China Coal Soc 27(03):268–272 (in Chinese)
Xu YS, Shen SL, Cai ZY, Zhou GY (2007) The state of land subsidence and prediction approaches due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Nat Hazards 45(1):123–135. doi:10.1007/s11069-007-9168-4
Xue YQ, Zhang Y, Ye SJ, Wu JC, Li QF (2005) Land subsidence in China. Environ Geol 48(6):713–720. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0010-6
Yang B, Gao D (1982) Determination of top boundary of fractured water-flowing zone by drilling simple hydrogeological method. Mine Surv 01:53–56 (in Chinese)
Yang ZZ, Wang JC, Lu FW (1994) Technical counter measures for coal mining under buildings, water-bodies and railways in Huainan coal mines. J China Coal Soc 19(1):05–14 (in Chinese)
Yin Z (2007) The principle of geotechnical engineering. China Water Power Press, Beijing
Yuan L, Wu K (2003) Theoretical research and technology practice on mining under the Huaihe River embankment. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou (in Chinese)
Yuan L, Wu K, Du G, Tan Z (2001) monitoring of Huaihe Dike deformation caused by mining. J China Univ Min Technol 11(01):14–19
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Liu S (1999) A new method of calculating surface subsidence and deformations under thick alluvial soil. Chin J Nonferrous Metals 09(02):435–440 (in Chinese)
Zhao H, Ma F, Zhang Y, Guo J (2012) Monitoring and analysis of the mining-induced ground movement in the Longshou Mine, China. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46(1):207–211. doi:10.1007/s00603-012-0232-3
Acknowledgments
The research has been financially supported by the National Engineering Laboratory of Mine Ecological Environmental Protection of Huainan Mining (Group) Co., Ltd, the Priority Academic Program Development of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) under Grant No. SZBF2011-6-B35, and the Graduate Scientific Research Innovation Program of the Jiangsu Province Ordinary University (CXLX13_945). All these financial supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, DW., Wu, K., Cheng, GL. et al. Mechanism of mining subsidence in coal mining area with thick alluvium soil in China. Arab J Geosci 8, 1855–1867 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1382-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1382-2