Abstract
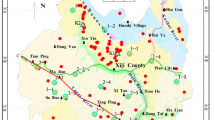
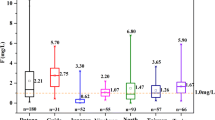
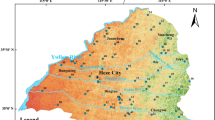
Hydrogeochemistry data were utilized to understand origin, distribution, and geochemical evolution of the high-fluoride groundwater in Taiyuan basin, China. In the study area, the spatial distribution of the high-fluoride groundwater are strictly controlled by the host rock and geomorphic conditions. Three types of groundwater with the F− concentration of <1.5 mg/L, 1.5–2 mg/L and >2 mg/L are located in the areas bordering the limestone zones, in the areas bordering the sandstone of Permian and Carboniferous, and in the depressions of the central parts of the basin, respectively. The high-fluoride groundwater mostly have the high values of TDS, and its values of pH range from 7.2 to 8.8. The most common water types of the high-fluoride groundwater are Na·Ca–HCO3 and Na·Mg–HCO3. The geochemical mode reveals that the dissolution of the fluorine-containing minerals and the evaporation effect of the shallow groundwater control the evolution of high F− concentration in Taiyuan basin.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Z (1985) Enrichment of fluoride in groundwater in the lower plain in the western area of Jilin province. Science Publishing House, Beijing, pp 43–47 (in Chinese)
Cao YQ (1997) The evaporation model of the high-fluoride water and its verification in the western area of Jilin, China. Eng Prospect 5:38–41
Gaciri SJ, Davies TC (1993) The occurrence and geochemistry of fluoride in some natural waters of Kenya. J Hydrol 143:395–412
Gao X, Wang Y (2007) Enrichment of fluoride in groundwater under the impact of saline water intrusion at the salt lake area of Yuncheng basin, northern China. Environ Geol 53:795–803
Gizaw B (1996) The origin of high bicarbonate and fluoride concentrations in waters of the main Ethiopian Rift Valley. J Afr Earth Sci 22:391–402
Gupta SK, Deshpande RD, Agarwal M, Raval BR (2005) Origin of high fluoride in groundwater in the North Gujarat-Cambay region, India. Hydrogeol J 13:596–605
Jacks G, Bhattacharya P, Chaudhary V, Singh KP (2005) Controls on the genesis of high-fluoride groundwaters in India. Appl Geochem 20:221–228
Kim K, Jeong YG (2005) Factors influencing natural occurrence of fluoride-rich ground waters: a case study in the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula. Chemosphere 58:1399–1408
Medina-Meja (2003) Un modelo Hidrogeoqumico del acufero de San Miguel de Allende (A hydrogeochemical model about the aquifer of San Miguel de Allende). Master thesis, Ciencias B_sicas, Universidad Iberoamericana, Leon
Nanyaro JT, Aswathanarayana U, Mungere JS, Lahermo P (1984) A geochemical model for the abnormal fluoride concentrations in waters in parts of northern Tanzania. J Afr Earth Sci 2:129–140
Oruc N (2003) Problems of high fluoride waters in Turkey (hydrogeology and health aspects). The short course on medical geology-health and environment. Canberra, Australia
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC(Version 2): a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey of Water Resources Investment Report, pp 99–4259
SGMB (Shanxi Geology and Mineral Bureau of China) (1985) Exploration and development of the groundwater resources in Taiyuan basin
Subba Rao N, John Devadas D (2003) Fluoride incidence in groundwater in an area of peninsular India. Environ Geol 45:243–251
Tian XY, Zhao DX (1984) The clay minerals from the Carboniferous strata containing coal beds in area from Taiyuan to Lingshi, Shanxi Province. Sci Geol Sin 1:80–86
Wang Y, Reardon EJ (2001) Activation and regeneration of a soil sorbent for defluoridation of drinking water. Appl Geochem 6:531–539
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. First addendum to third edition, Volume 1, Recommendations. World Health Organization
Zhang N (2001) Distribution of fluoring and its affecting factors in soil in Shanxi. Acta Pedol Sin 38(2):284–287
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the project of National Natural Science Funds of China (40672169). Thanks Zhenzhong Guo of the Shanxi Geology and Mineral Bureau for supplying us with useful reports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Hou, X., Zhou, Z. et al. Geochemical provenance and spatial distribution of fluoride in groundwater of Taiyuan basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 62, 1635–1642 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0648-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0648-6