Abstract
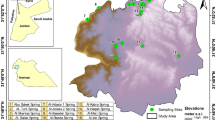
The origin of the high salinity in the groundwater of a coastal wetland in an arid climate was studied in the Playa Fracasso marsh, located on the northwest coast of the extra-Andean Patagonia. Research was carried out by means of the design of a network of soil pits and short piezometers in the marsh and the surrounding landforms. Continuous fluctuations of the water table, in situ physical and chemical properties, major ions (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, Cl−, SO4 2−, HCO3 −) and stable isotopes (18O and 2H) in groundwater, as well as soil salinity, were measured. The combined analysis of the hydrodynamics, the ion ratios rCa2+/rCl− and rMg2+/rCa2+ vs. rCl− and the isotopic composition made it possible to recognize an area within the high marsh in which the origin of groundwater is mainly marine and another in which the contributions are of mixed origin. By means of the analysis of rCl− vs. δ18O, a salinization process with no change in isotopic composition was identified. Its interpretation, together with those of the soil salinity profiles and the records of the fluctuations in electrical conductivity associated with extraordinary tides, was used to define a conceptual model of salinization which could be useful to understand other coastal wetlands under similar arid climatic conditions. It consists in a cyclical mechanism of evapotranspiration, precipitation, dissolution and transport of salts during tides.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam P (1990) Salt marsh ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Alvarez MP, Weiler N, Hernández MA (2010) Linking geomorphology and hydrodynamics: a case study from Peninsula Valdés, Patagonia. Argent Hydrogeol J 18:473–486
Alvarez MP, Dapeña C, BouzaP, Hernández MA (2012) Estudio químico e isotópico preliminar del origen del agua subterránea en el humedal costero Playa Fracasso. Península Valdés, Chubut. II Reunión Argentina de Geoquímica de la Superficie. IADO. CONICET-UNS. Bahía Blanca. Abstract book. GI-1
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1997) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, p 1134
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2005) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group. 241–247
Bala LO, Hernández MA, Musmeci LR (2008) Humedales costeros y aves playeras migratorias. CENPAT, Puerto Madryn, p 120. ISBN:978-987-05-5598-8
Bortolus A, Schwindt E, Bouza PJ, Idaszkin YL (2009) A characterization of Patagonian Salt Marshes. Wetlands 29(2):772–780
Bouza PJ, Sain C, Bortolus A, Ríos I, Idaszkin Y, Cortés E (2008) Geomorfología y características morfológicas y fisicoquímicas de suelos hidromórficos de marismas patagónicas. Actas XXI Congreso Argentino de la Ciencia del Suelo, San Luis. CD-ROM edition
Brinson MM (1989) Fringe wetlands in Albemarle and Pamlico sounds: landscape position, fringe swamp structure, and response to rising sea level. Project No. 88-14, Albemarle-Pamlico Estuarine Study, Raleigh
Burgos JJ, Vidal AL (1951) Los climas de la República Argentina, según la nueva clasificación de Thornthwaite. Meteoros 1:3–32
Bye JAT, Narayan KA (2009) Groundwater response to the tide in wetlands: observations from the Gillman Marshes, South Australia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 84:219–226
Carol E, Kruse E, Mas-Pla J (2009) Hydrochemical and isotopical evidence of ground water salinization processes on the coastal plain of Samborombón Bay. Argent J Hydrol 365:335–345
Carol E, Mas-Pla J, Kruse E (2013) Interaction between continental and estuarine waters in the wetlands of the northern coastal plain of Samborombón Bay. Appl Geochem 34:152–163
Castillo Pérez E, Morell Evangelista I (1988) La hidroquímica en los estudios de intrusión marina en los acuíferos españoles. TIAC’88, 19–73
Codignotto JO (1987) Glosario Geomorfológico Marino. Asociación Geológica Argentina, Serie B: Didáctica y Complementaria No. 17, p 70
Custodio E (1997) Studying, monitoring and controlling seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. In: guidelines for study monitoring and control. FAO Water Reports. p 11
Custodio E (2010) Las aguas subterráneas como elemento básico de la existencia de numerosos humedales. Ingeniería del Agua 17:119–135
Dapeña C (2008) Isótopos ambientales livianos: su aplicación en hidrología e hidrogeología. PhD thesis. Departamento de Ciencias Geológicas, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires. Tesis 4282. p 442
Dapeña C, Panarello HO (1999) Development of the National Network for Isotopes in Precipitation of Argentina. II South American Symposium on Isotope Geology 503–508
Dapeña C, Panarello HO (2008) Isótopos en precipitación en Argentina. Aplicaciones en Estudios Hidrológicos e Hidrogeológicos. IX Congreso Latinoamericano de Hidrología Subterránea. ALHSUD Volumen CD T-100. p 8. Quito, Ecuador
de Montety V, Radakovitch O, Vallet-Coulomb C, Blavoux B, Hermitte D, Valles V (2008) Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in a confined coastal aquifer: case of the Rhône delta (Southern France). Appl Geochem 23(2008):2337–2349
Durán JJ (2003) Presencia de aguas de diferente salinidad y origen en los humedales del litoral mediterráneo español. In: Tecnología de la intrusión de agua de mar en acuíferos costeros: países mediterráneos, 2:149–154. Serie: Hidrogeología y Aguas Subterráneas, 8, IGME. Madrid
Erskine AD (1991) The effect of tidal fluctuations on a coastal aquifer in the UK. Ground Water 29:556–562
Fass T, Cook PG, Stieglitz T, Herczeg AL (2007) Development of saline groundwater through transpiration of sea water. Ground Water 45(6):703–710
Ferris JG (1951) Cyclic fluctuations of water level as a basis for determining aquifer transmissibility: Int Geodesy Geophys Union, Assoc Sci Hydrol Gen. Assembly, Brussels, 2: 148–155; duplicated 1952 as US Geological Survey Ground Water Note 1
Fitzpatrick RW, Merry RH, Cox JW (2000) What are saline soils? What happens when they are drained? J Aust Assoc Nat Resour Manag (AANRM). Special Issue (June 2000), 26–30
Frumento O, Contrera O (2013) Laboratorio de climatología Centro Nacional Patagónico—CONICET, Puerto Madryn. http://cenpat-conicet.gov.ar/fisicambien/Rep_Clim_Mens.htm
Gat JR (1981) Groundwater. In: stable isotope hydrology: deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle. Technical report series No 210, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Chapter 10:223–240
Gonfiantini R (1978) Standards for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds. Nature 271:534
Gonfiantini R, Araguas-Araguas L (1988) Los isótopos ambientales en el estudio de la intrusión marina. Tecnología de la intrusión en acuíferos costeros, vol 1, 135–190. Inst Geol y Minero de España, Madrid
Haller M, Monti A, Meinster C (2001) Hoja Geológica 4366-1 Península Valdés. Boletín Nro. 266. Buenos Aires: Servicio Geológico Minero Argentino
Han DM, Kohfahl C, Song XF, Xiao GQ, Yang JL (2011) Geochemical and isotopic evidence for paleo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay. China Appl Geochem 26:863–883
Harbison J, Cox M (2002) Hydrological characteristics of groundwater in a subtropical coastal plain with large variations in salinity, Pimpana, Queensland. Aust Hydrol Sci J 47(4):651–665
Hidrografía Naval Argentina (2010–2012) Tablas de marea. http://www.hidro.gov.ar/oceanografia/Tmareas/Form_Tmareas.asp
IAEA/WMO (2002) Global network for isotopes in precipitation. The GNIP Database. http://isohis.iaea.org
Lee JY, Song SH (2007) Groundwater chemistry and ionic ratios in a western coastal aquifer of Buan, Korea: implication for seawater intrusion. Geosci J 11(3):259–270
Lis G, Wassenaar LI, Hendry MJ (2008) High-precision laser spectroscopy D/H and 18O/16O measurements of microliter natural water samples. Anal Chem 80:287–293
Manzano M, Borja F, Montes C (2002) Metodología de tipificación hidrológica de los humedales españoles con vistas a su valoración funcional y a su gestión. Aplicación a los humedales de Doñana. Boletín Geológico y Minero, 113(3):313–330
Mitsch WJ, Gosselink JG (2000) Wetlands, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Ridd PV, Stieglitz T (2002) Dry season salinity changes in arid estuaries fringed by mangroves and saltflats. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54(6):1039–1049
Ríos I (2010) Geoecología de plantas vasculares en suelos hidromórficos de una marisma patagónica: propiedades morfológicas, físicas, químicas y bióticas. Universidad Nacional de la Patagonia San Juan Bosco, Puerto Madryn, p 57
Ríos I, Bouza PJ, Sain CL, Bortolus A, Cortés EG (2012) Caracterización y clasificación de los suelos de una marisma patagónica, NE del Chubut. XIX Congreso Latinoamericano de Suelos and XXIII Congreso Argentino de la Ciencia del Suelo. Mar del Plata, Argentina. Extended abstract. CD-ROM. ISBN 978-987-1829-11-8
Schlumberger (2010) AquaChem 2010.1. A professional application for water quality analysis, plotting, replotting and modeling. Schlumberger Water Services
Silvestri S, Marani M (2004) Salt-marsh vegetation and morphology: basic physiology, modelling and remote sensing. In: Fagherazzi S, Blum L, Marani M (eds) Ecogeomorphology of tidal marshes. American Geophysical Union, Coastal and Estuarine Monograph Series Observations, Washington
Smith AJ, Hick WP (2001) Hydrogeology and aquifer tidal propagation in Cockburn sound, Western Australia. CSIRO Technical report 6/01
Soil Survey Staff (1999) Soil taxonomy. A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys; second edition. Agricultural Handbook 436; Natural Resources Conservation Service, USDA, p 869, Washington
Thornthwaite CW, Mather JR (1957) Instructions and tables for computing potential evapotranspiration and water balance. Centerton, p 312
Vázquez Suñé E (2002) Programa Easy Quim 4. GHS-UPC, CIHS, Spain
Vengosh A (2003) Salinization and saline environments. In: Sherwood Lollar B, Holland HD, Turekian KT (eds) Environ Geochem. Elsevier Science. 9:333–365
Warner N, Lgourna Z, Bouchaou L, Boutaleb S, Tagma T, Hsaissoune M, Vengosh A (2013) Integration of geochemical and isotopic tracers for elucidating water sources and salinization of shallow aquifers in the sub-Saharan Drâa Basin, Morocco. Appl Geochem 34:140–151
Wilson AM, Morris JT (2012) The influence of tidal forcing on groundwater flow and nutrient exchange in a salt marsh-dominated estuary. Biogeochemistry 108(1–3):27–38. doi:10.1007/s10533-010-9570-y
Yurtsever Y (1994) Role of environmental isotopes in studies related to salinization processes and salt water intrusion dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 13th Salt-Water Intrusion Meeting, Cagliari. pp 177–185
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Agr. Eng. Claudia Saín for her assistance in the laboratory and Tech. Julio César Rua (Bocha) for his help in the field. This work has been funded by the ANPCyT (PICT2008 No 2127) and the CIUNPAT-UNPSJB-PROPEVA (PI No 842).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, M.d.P., Dapeña, C., Bouza, P.J. et al. Groundwater salinization in arid coastal wetlands: a study case from Playa Fracasso, Patagonia, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 73, 7983–7994 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3957-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3957-3