Abstract
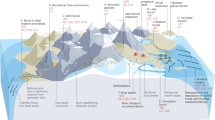
Field measurements of the processes of dispersion of concentrated suspended silts over the active delta front of the Yellow River (China) show that cross-isobath sediment dispersal into the shallow Bohai Gulf is dominated by gravity-driven underflows. These underflows descend the rapidly programing delta front as hyperpyc-nal plumes 1–4 m thick. The widespread, dilute plumes observed during the summer flood season deposited most of their sediment and experienced extinction between the 5-m and 10-m depth con-tours. High-frequency internal waves on the upper interface of the underflows may have contributed to the rapid deceleration. Muds resuspended by an intense autumn storm caused denser, but short-lived, plumes which extended downslope to depths of over 13 m.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pallesen, T. R. Turbidity Currents. Institute of Hydrodynamics and Hydraulic Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, Series Paper 32, 115 pp (1983).
Siegenthaler, C. & Buhler, J. Mar. Geol. 64, 19–40 (1985).
Komar, P. D. in The Sea: Marine Modelling, Vol. 6 (eds Goldberg, E. D., McCave, I. N., O'Brien, J. J. & Steele, J. H. 603–621 (Wiley, New York, 1977).
Seymour, R. J. Ocean Engng 13, 435–447 (1986).
Wright, L. D. et al. Geo. Mar. Lett. 6, 151–174 (1986).
Curtin, T. B. & Legeckis, R. V. Cont. Shelf Res. 6, 31–51 (1986).
Keller, G. H. & Prior, D. B. Geo. Mar. Lett. 6, 63–120 (1986).
Qin, Y. & Li, F. Proc. Int. Symp. on Sedimentation on the Continental Shelf with Special Reference to the East China Sea 1, 91–101 (Hangzhou China, 1983).
Ren, M. & Shi, Y.-L. Cont. Shelf Res. 6, 785–810 (1986).
Bornhold, B. D. et al. Geo. Mar. Lett. 6, 77–83 (1986).
Wright, L. D. et al. Geo. Mar. Lett. 6, 115–120 (1986).
Yang, Z.-S. & Lu, Z. Eos 68, 1735 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, L., Wiseman, W., Bornhold, B. et al. Marine dispersal and deposition of Yellow River silts by gravity-driven underflows. Nature 332, 629–632 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/332629a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/332629a0
This article is cited by
-
The controlling factors of high suspended sediment concentration in the intertidal flat off the Huanghe River Estuary
Acta Oceanologica Sinica (2020)
-
Geochemical and Grain-Sized Implications for Provenance Variations of the Central Yellow Sea Muddy Area Since the Middle Holocene
Journal of Ocean University of China (2020)
-
Reply to discussions by Zavala (2019) and by Van Loon, Hüeneke, and Mulder (2019) on Shanmugam, G. (2018, Journal of Palaeogeography, 7 (3): 197–238): ‘the hyperpycnite problem’
Journal of Palaeogeography (2019)
-
Numerical Study on Seasonal Transportation of the Suspended Sediments in the Modern Yellow River Mouth Effected by the Artificial Water and Sediment Regulation
Journal of Ocean University of China (2019)
-
The hyperpycnite problem
Journal of Palaeogeography (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.