Options
Role of cell cycle on the cellular uptake and dilution of nanoparticles in a cell population
Date Issued
2012-01
Date Available
2012-06-21T15:51:16Z
Abstract
Nanoparticles are considered a primary vehicle for targeted therapies because they can pass biological barriers, enter and distribute in cells by energy-dependent pathways1-3. Until now, most studies have shown that nanoparticle properties, such as size4-6 and surface7,8, can affect how cells internalise nanoparticles. Here we show that the different phases of cell growth, which constitute the cell cycle, can also influence nanoparticle uptake. Although cells in different cell cycle phases internalised nanoparticles with similar rates, after 24 hours of uptake the concentration of nanoparticles in the cells is ranked according to the different cell cycle phases: G2/M > S > G0/G1. Nanoparticles were not exported from cells but the internalised nanoparticle concentration is split when the cell divides. Our results suggest that future studies on nanoparticle uptake should consider the cell cycle because in a cell population, the internalised nanoparticle dose in each cell varies as the cell cycles.
Sponsorship
Science Foundation Ireland
Higher Education Authority
Irish Research Council for Science, Engineering and Technology
European Research Council
Type of Material
Journal Article
Publisher
Nature Publishing Group
Journal
Nature Nanotechnology
Volume
7
Issue
1
Start Page
62
End Page
68
Copyright (Published Version)
© 2011 Nature Publishing Group
Subjects
Subject – LCSH
Nanoparticles
Nanomedicine
Cell cycle
Language
English
Status of Item
Peer reviewed
ISSN
1748-3387
This item is made available under a Creative Commons License
File(s)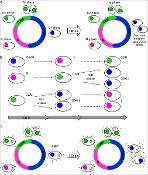
Loading...
Name
scheme 1 final.tif
Description
Scheme figure
Size
740.85 KB
Format
TIFF
Checksum (MD5)
12e6c70b04049231ce1ec82b8002edef
No Thumbnail Available
Name
Manuscript_black.doc
Description
Main article
Size
232.5 KB
Format
Microsoft Word
Checksum (MD5)
5f03f336bcba758cdd1c9af139691dea
Owning collection
Mapped collections